
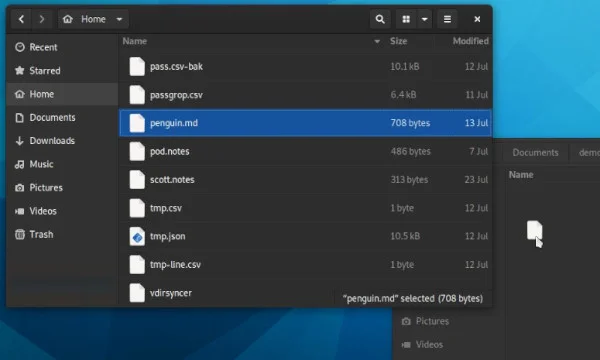
When the file is renamed with mv command then the inode number remains the same even after moving it to a different file name. The syntax for the mv command is as follows: mv OPTIONS SOURCE DESTINATION The SOURCE can be one, or more files or directories, and DESTINATION can be a single file or directory. Given below are the examples of mv command in Linux: Example #1 – Rename the File. The mv command (short from move) is used to rename and move and files and directories from one location to another. This option will be useful if we need to overwrite multiple sets of files whose permission is read-only and if you do not specify this option then prompt will appear for every file. mv -f, –force: This option will move the files or directories without any prompt. mv –version: This option checks the version of mv command.Ĩ. mv –suffix=suffix: This option is used to take a backup of the files or directories before overwriting it. mv *: This option will move multiple files to a specific/current directory.Ħ. mv -u: This option implies as “update mode”, means it will update the destination file is missing only when the source file has any new content or even when the destination file is missing.ĥ. mv -v: It means moving the file in “verbose mode”, means it will display the activity status happening while mv command is running.Ĥ. In simple terms, we can rename a file to match another file and still keep the content of the already existing file.ģ. mv -n: This option used as no-clobber which implied that it will prevent a file from overwriting.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/011-move-files-with-linux-mv-command-2201103-cc2df69a72ec4037b577d2ef8bc0aa62.jpg)
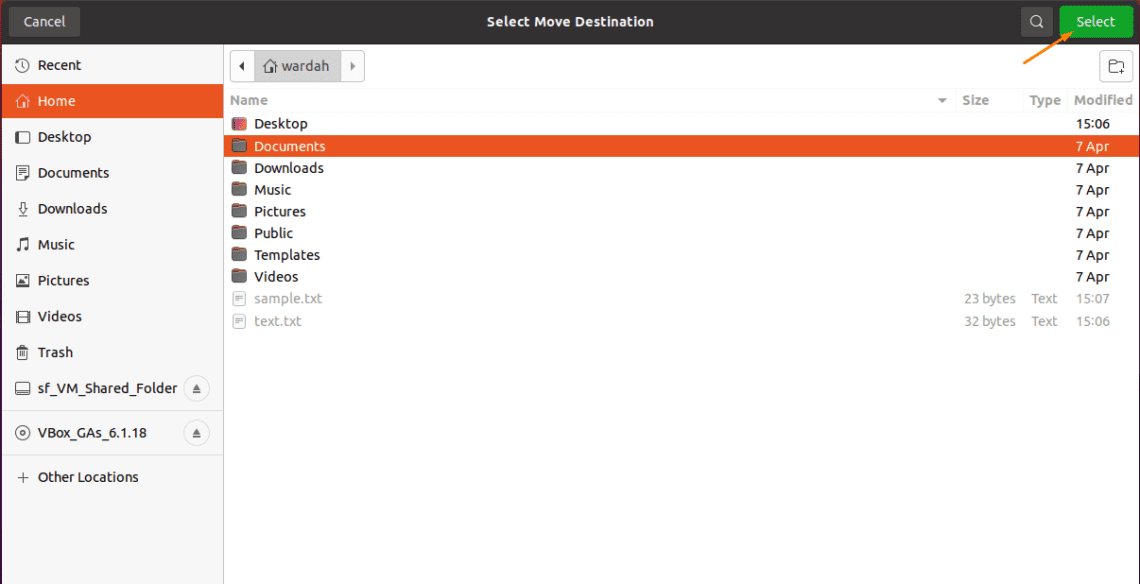
In this scenario, we have to enter “y” to confirm or overwrite the file.Ģ. mv -i: This option signifies “Interactive Mode”, means that it will prompt the user’s confirmation before moving a file that will replace/overwrite already existed file with the same name.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
